Anatomy of a Layout
Introduction
The view shown by jDownloads on the front end uses various areas of the active layouts. These play the same role as a Template in setting the general view of your site. Like a template, the layouts are written in HTML code and make use of CSS structures. It is assumed here that you have either read the article 'An Introduction to Layouts' (opens in a new window/tab) or are reasonably familar with layouts.
There are 7 types of layout (Categories, Subcategories, Category, Downloads, Download Details, Summary and Search).
For each type only one layout may be selected as active. Each Layout has, in principle, two sections . One section has the header, subheader and footer sub-sections and the other section has the before, main and aftersub-sections. So the view on the screen uses appropriate section from the available active layouts.
There are 7 types of layout (Categories, Subcategories, Category, Downloads, Download Details, Summary and Search).
For each type only one layout may be selected as active. Each Layout has, in principle, two sections . One section has the header, subheader and footer sub-sections and the other section has the before, main and aftersub-sections. So the view on the screen uses appropriate section from the available active layouts.
One of the key aspects of layouts are the 'placerholders'. These are like small "plugins" or "macros" that generate the relevant code. They appear in layout code enclosed in braces: { and }. For instance the placeholder {category_listbox} generates the code that will show a pulldown list of all the categories and sucategories.
Also please note that not every placeholder is available in every type of layout. When you open a layout in the back end then each section has an
To access the layouts in the Joomla control page click on  then click on
then click on  and then click on
and then click on  . This takes you to the main Layouts page which has a set of tabs of the layout types and the CSS files as shown immediatley below.
. This takes you to the main Layouts page which has a set of tabs of the layout types and the CSS files as shown immediatley below.
 If you click on a layout type such as for example
If you click on a layout type such as for example  then it shows a list of all of the Layouts of that type
then it shows a list of all of the Layouts of that type
 If you click on a layout type such as for example
If you click on a layout type such as for example 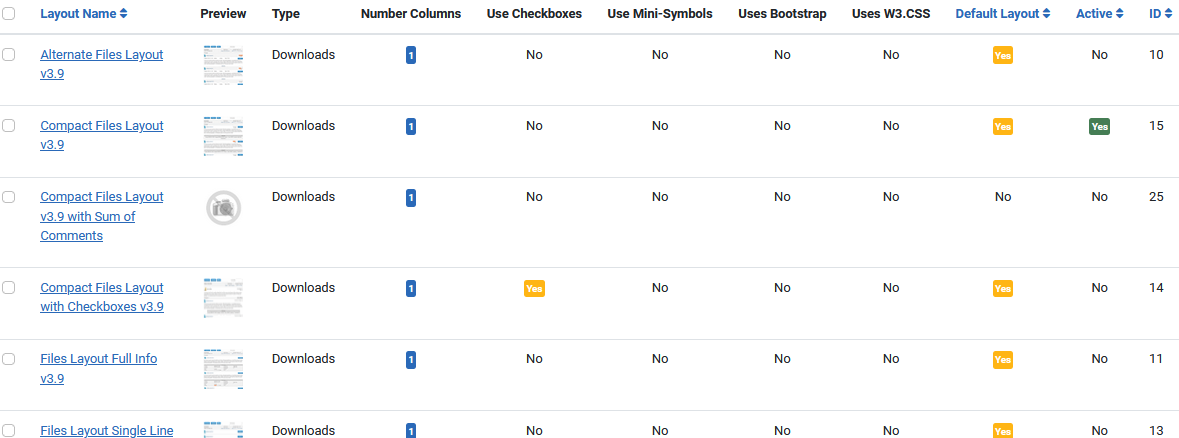
If you click on the name of a layout then the details on that layout will be shown as discussed below.
Switching the view between the two section is by clicking on either the tab or the
tab or the  tab.
tab.
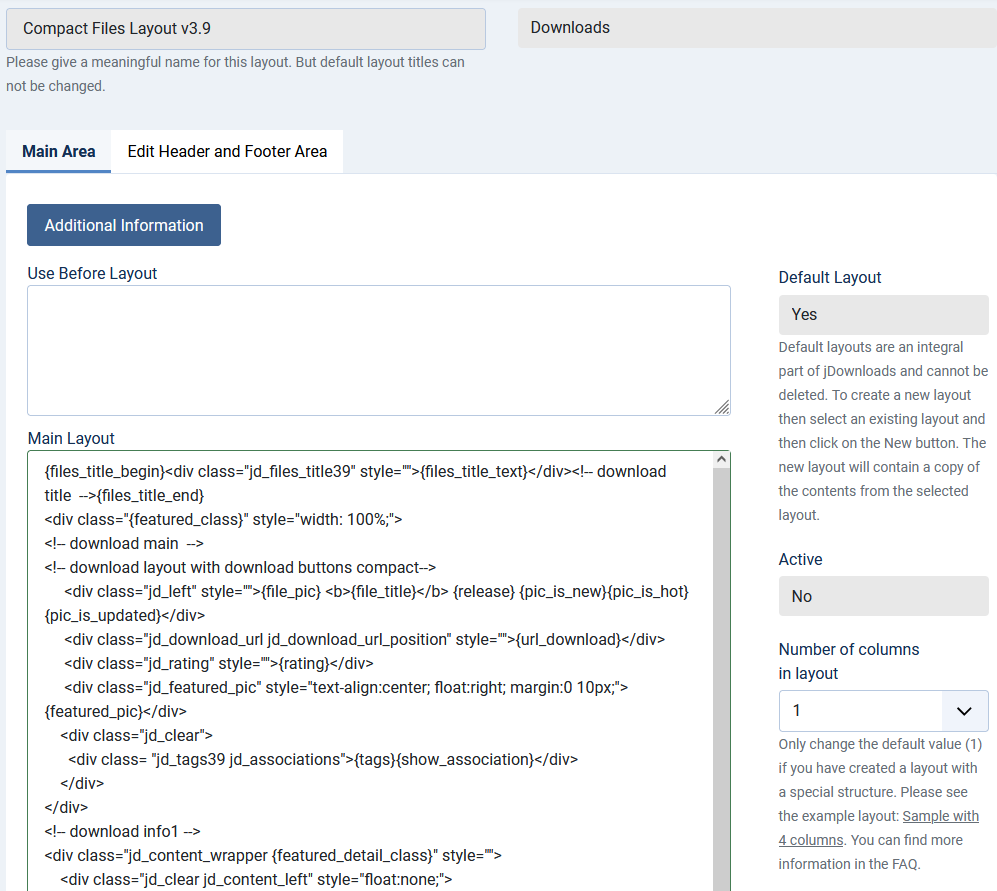
In this example there is no code in the 'Use Before Layout' or the 'Use After Layout'. The has most of the code.
has most of the code.
Switching the view between the two section is by clicking on either the
In this example there is no code in the 'Use Before Layout' or the 'Use After Layout'. The
Main area
The main area has most of the code. It also has a side bar. Note the image below is quite long as it shows all of the sidebar and most of the layout main code! It has three areas: 'Use Before Layout', the 'Main Layout' itself and the 'Use After Layout'. In this example the 'Use Before Layout' and the 'User After Layout' are both empty.
Also notice the button.
button.
Also notice the
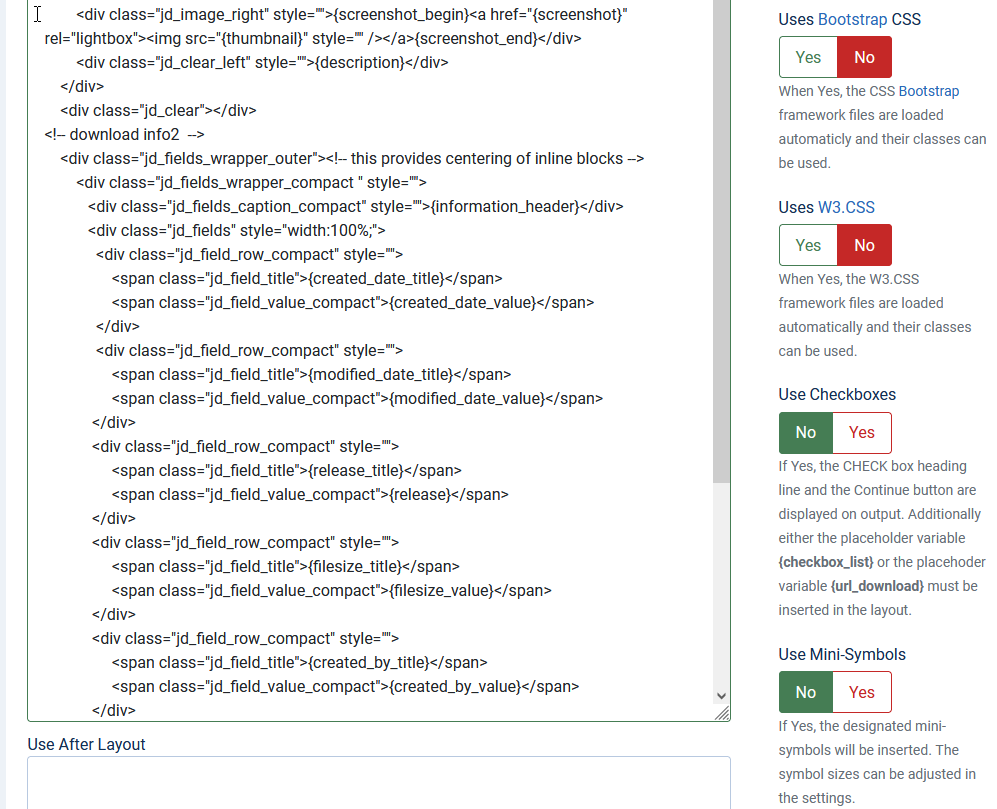

In the code sections there are so called placeholders such as {file_pic}. These placeholders call internal routines that carry out the relevant action, which in this case show an image of the file type such as  .
.
The panel on the right hand side as illustrated earlier provides information and options for the layout.
It shows if it is a default layout, that is whether or not the layout is part of the jDownloads installation. Also whether this layout is the current Active layout of this type.
There is also a facility to load in two additional popular CSS framework files to allow additional classes and the like for 'own' styling.
Please note if you do plan to modify an existing layout always make a copy first by using the button and then modify that new one.
button and then modify that new one.
If the Title of the original one was say "Standard Files Layout without Checkboxes 3.9" then the copy will be "Standard Files Layout without Checkboxes 3.9 (2)". You may of course change the Title.
There is also a description box where you can add details about the layout. This description will appear on the main layout panel in the backend.
It shows if it is a default layout, that is whether or not the layout is part of the jDownloads installation. Also whether this layout is the current Active layout of this type.
There is also a facility to load in two additional popular CSS framework files to allow additional classes and the like for 'own' styling.
Please note if you do plan to modify an existing layout always make a copy first by using the
 button and then modify that new one.
button and then modify that new one. If the Title of the original one was say "Standard Files Layout without Checkboxes 3.9" then the copy will be "Standard Files Layout without Checkboxes 3.9 (2)". You may of course change the Title.
There is also a description box where you can add details about the layout. This description will appear on the main layout panel in the backend.
Placeholders
Click on the  button to see the list all of the placeholders, which are always enclosed in { } characters, that are available for the current section of the layout type that is currently being shown.
button to see the list all of the placeholders, which are always enclosed in { } characters, that are available for the current section of the layout type that is currently being shown.
The Downloads type layouts have by far the largest number of placeholders. The example below shows the placeholders available in the main area. In general one would not use placeholders in the before and after areas.
The Downloads type layouts have by far the largest number of placeholders. The example below shows the placeholders available in the main area. In general one would not use placeholders in the before and after areas.
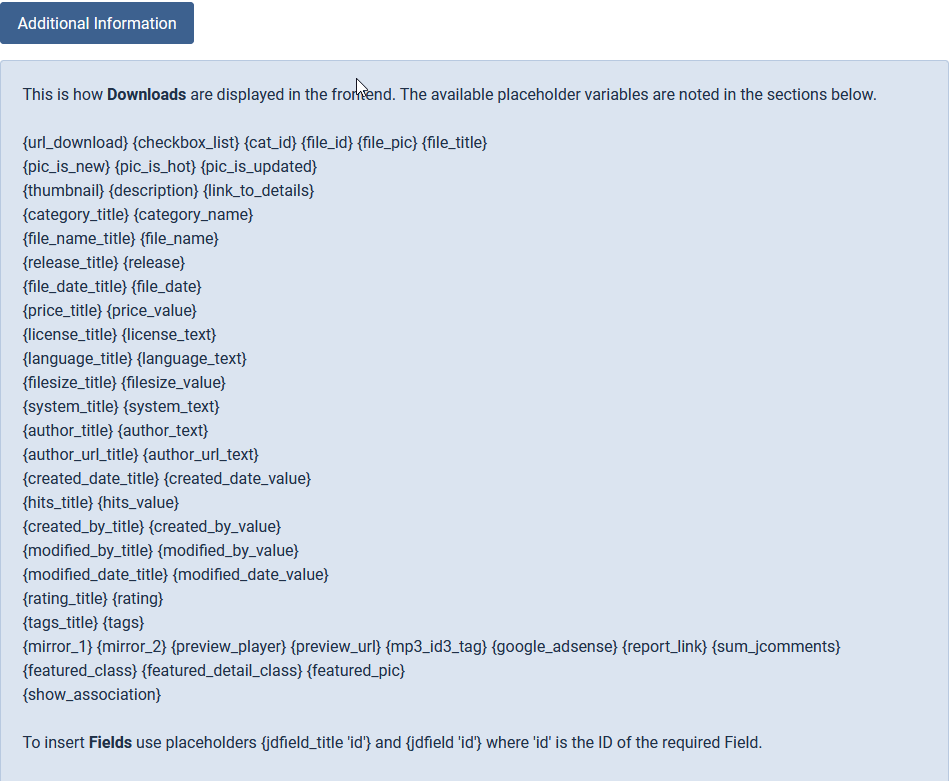

The image below shows the placeholders available for the the header, subheader and footer areas.

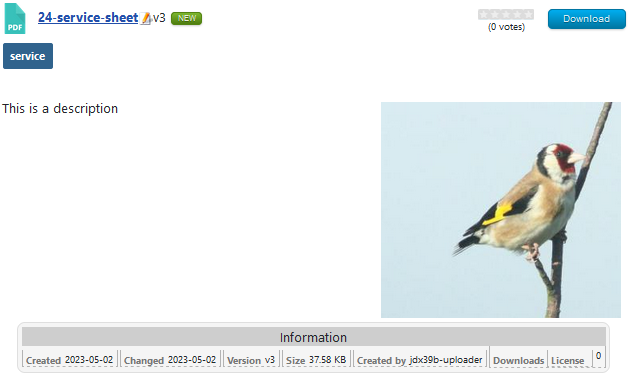
Before looking in detail at the layout anatomy it is useful to first see a typical view showing Downloads.
The image opposite shows an example view of the contents of a single category.
The active Downloads layout is "Compact Files Layout 3.9".
Because it is a view of a single category the outer framework, that is the header and footer areas, come from the active Category layout.
The subheader comes from the active Downloads style. Similarly each of the three Downloads come from repeated use of the main area of the active Downloads style.
The image opposite shows an example view of the contents of a single category.
The active Downloads layout is "Compact Files Layout 3.9".
Because it is a view of a single category the outer framework, that is the header and footer areas, come from the active Category layout.
The subheader comes from the active Downloads style. Similarly each of the three Downloads come from repeated use of the main area of the active Downloads style.

In the following examples the HTML code has been 'coloured' for clarity.
In the code fragments you will also see lines like These clear the space below them, they may be thought of as creating a new line.
These clear the space below them, they may be thought of as creating a new line.
In the code fragments you will also see lines like
Header
For example a typical Header would look like the top image opposite whilst the HTML in the layout to generate this is in the second image.
The correspondance between the code and the view on the screen is evident.
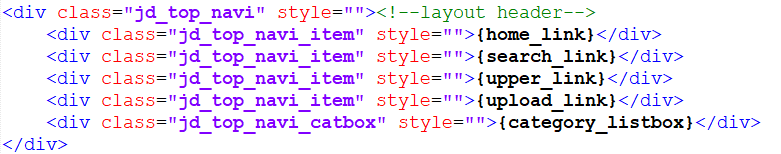
The correspondance between the code and the view on the screen is evident.


Subheading
The subheading area shows the details of the Category that contains the Downloads.
The Navigation only shows if there are more Downloads than the value in the Options - Frontend tab - 'Number of Downloads to show per page' setting.
Similarly the Sort order bar will only show if Options - Frontend tab -'View sort option in the header' is set to Yes and also that 'Select the fields for the sort bar' is not empty.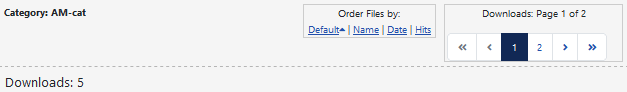
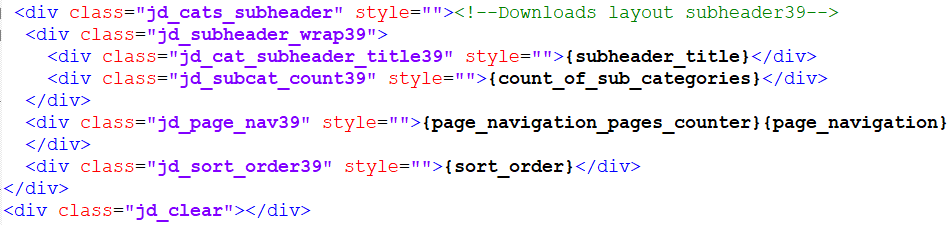
The Navigation only shows if there are more Downloads than the value in the Options - Frontend tab - 'Number of Downloads to show per page' setting.
Similarly the Sort order bar will only show if Options - Frontend tab -'View sort option in the header' is set to Yes and also that 'Select the fields for the sort bar' is not empty.


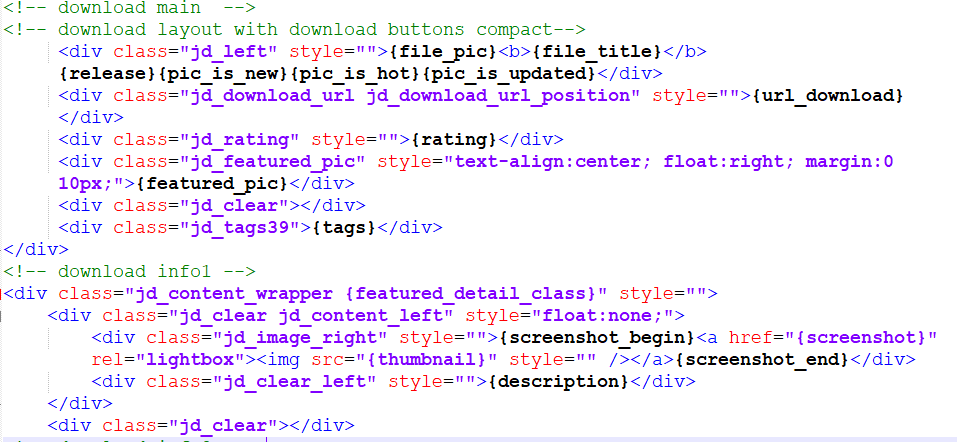
Main
The top line of the Download view has various icons, a title and the download button. Underneath those is a tag.
Then there is some descrption on the left and an image on the right.
As previously the code may readily be related to the view because of the names of the CSS classes and the placeholders.
In this example there were no 'ratings' in use and also the Download was not 'featured' so those sections of code generate no output.
For more information on making a Download featured see Featuring a Download (opens in a new window/tab).

Then there is some descrption on the left and an image on the right.
As previously the code may readily be related to the view because of the names of the CSS classes and the placeholders.
In this example there were no 'ratings' in use and also the Download was not 'featured' so those sections of code generate no output.
For more information on making a Download featured see Featuring a Download (opens in a new window/tab).


The Next section of the Download view is the information section.
Although in this compact view it is only one line, the actual code to generate the view is quite extensive.
Each placeholder is shown on a seperate line in the code to make it simpler to understand.
One of the most frequent reasons for making a copy of the layout and then editing the copy is to change which placeholders are more appropriate for your site.
Also adding or removing entries to the view is straightforward by adding or removing code 'blocks' such as
 Also note that if the available screen width is too small then it will automatically wrap.
Also note that if the available screen width is too small then it will automatically wrap.

Although in this compact view it is only one line, the actual code to generate the view is quite extensive.
Each placeholder is shown on a seperate line in the code to make it simpler to understand.
One of the most frequent reasons for making a copy of the layout and then editing the copy is to change which placeholders are more appropriate for your site.
Also adding or removing entries to the view is straightforward by adding or removing code 'blocks' such as
 Also note that if the available screen width is too small then it will automatically wrap.
Also note that if the available screen width is too small then it will automatically wrap.


The last section of the main part is the preview. This will show either a video or an audio, of if there is no preview then nothing is shown.
The code is basically just one line. The placeholder {preview} uses the file extension of the preview file to determine which type of player to show.
The other placeholder {mp3_id3_tag} will only show for mp3 type previews.
.png)
.png)
Footer
The last part of any view is the footer.
It shows the back link button and the navigation if in Options - Frontend tab - 'Show navigation at the bottom' is set to Yes.
.png)
.png)
It shows the back link button and the navigation if in Options - Frontend tab - 'Show navigation at the bottom' is set to Yes.
.png)
.png)
In most of the HTML code the <div lines include a statement style="". This enables changing simple matters such as say font-size by directly including the relevant CSS inside the "". See W3 use of HTML inline style (opens in a new window/tab) for more information.
ColinM February 2020 modified July 2023
 ownloads Documentation Centre!
ownloads Documentation Centre!